The selection of fuel burners for oil and gas boilers should be based on the structural characteristics and performance requirements of the boiler body, as well as fuel characteristics, and combined with user usage conditions.
As the combustion equipment of fuel and gas boilers, the burner’s main function is to:

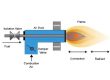
Gas and oil boiler burners
- Provide the fuel or gas required for the boiler, and choose the oil atomization method to increase the contact area between the fuel and air. The combustion method should also be selected for gas fuels
Supply the necessary air for combustion, achieve full mixing of air with oil mist or gas, and ensure full combustion - Ensure rapid ignition and stable combustion
- Implement automatic control of program ignition and combustion processes
At present, the oil and gas burners used for small and medium-sized boilers mostly adopt an integrated structure, so people commonly refer to them as burners.
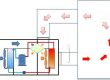
The oil burner is mainly composed of housing, electric motor, fan, damper, damper actuator, oil pump, solenoid valve, ignition electrode assemblies, flame detector, oil nozzle, etc.
A gas burner mainly consists of housing, electric motor, gas nozzle, fan, damper, solenoid valve, ignition electrode, flame sensor, etc.
The electric motor is connected to the fan and oil pump through a coupling, and when the electric motor rotates, it drives the fan and oil pump to rotate at the same time. The function of the fan is to send the air required for combustion into the furnace and generate a certain amount of pressure.
Adjusting the air door regulator can control the opening of the air intake door to adjust the air intake volume. The function of the oil pump is to pressurize the fuel oil and provide energy for atomization.
The solenoid valve switch is for controlling the supply of fuel oil or gas. The number of oil nozzles or gas nozzles for small burners can be one or several, and they are controlled by different solenoid valves to achieve different stage of combustion.
The flame monitor serves as a safety ignition and flameout protection. In addition, each burner is equipped with a burner controller, and the ignition and operation program of the burner is controlled through it.
Although the working principle and structure of burners are roughly the same, there are significant differences in the performance of burners produced by different structures or manufacturers. Therefore, when selecting burners, attention should be paid to the following aspects:
The burner output needs to be matched with the boiler capacity and the boiler smoke and air resistance
Due to the compact structure and convenient installation of the integrated burner, which does not require additional equipment such as fans and oil pumps, it has been widely used in small and medium-sized oil and gas boilers.
Most boilers adopt positive pressure combustion and operation, that is, the inlet air of the boiler is fed into the furnace by the fan of the burner, and the flue gas generated by combustion is also blown out of the furnace chamber and discharged into the atmosphere by the pressure generated by the fan.
At this point, if the pressure of the selected burner is less than the smoke and air resistance of the boiler system, the burner cannot blow the smoke out of the furnace, nor can it send air into the furnace, thus unable to ensure normal combustion.
However, there is a certain relationship between the pressure of the burner and the thermal power (or fuel consumption) of the burner. When selecting a burner, it is necessary to consider both the matching of the burner thermal power and the boiler output, as well as the matching of the burner pressure and the resistance of the smoke and air system. Both are indispensable.
When selecting a burner, it should first be based on the type of fuel, such as liquid fuels such as kerosene, diesel, heavy oil, residual oil, and waste oil.
Gas fuels include urban gas, natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, and biogas. The following characteristics of fuel should be understood:
- Kerosene and diesel should have heating and density parameters
- There should be parameters of heavy oil, residual oil, waste oil, viscosity, heat generation, moisture content, flash point, mechanical impurities, ash content, freezing point and density.
- Gas should have parameters such as heat generation, supply pressure, and density
When understanding the characteristics of the fuel, priority should be given to selecting a burner that can adapt to the fuel. Such as light oil burners, heavy oil burners, residual oil burners, or natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas burners, etc. Then estimate the fuel consumption roughly based on the heat value of the fuel, in order to select the specific model of the burner。
When selecting a burner without fuel heating value, it can be determined by converting the boiler output into thermal power. However, each model of burner has a range of fuel or gas consumption. If the fuel or gas consumption of the selected burner cannot meet the fuel consumption required by the boiler, the output of the boiler cannot be guaranteed
 +8613906047998
+8613906047998