The growth code of CO2 heat pumps
The popularity of CO2 heat pump technology continues to rise. Recently, CO2 heat pump technology has been included in China’s national energy development key examination plan. In the future, it is expected to receive more resources in terms of heat pump project approval and financial support, laying a solid policy foundation for the growth of its heat pump industry.
In addition, the world’s largest CO2 seawater heat pump system in Denmark was started, with a heating capacity of 70 megawatts. It can supply about 280,000 megawatt-hours of heat energy each year, meeting the winter heating needs of about 25,000 households, becoming a model in the field of green heating.
Key factor: heat pumps’ excellent environmental performance
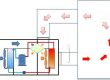
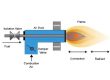
CO2 heat pump technology uses CO2 as a refrigerant to transfer heat energy from a low-temperature environment to a high-temperature environment through an efficient heat exchange process, thereby achieving the purpose of heating or cooling.
Compared with traditional heat pump systems, CO2 heat pumps have a higher energy efficiency ratio, can maintain efficient heating capacity in low temperature environments, and significantly reduce energy consumption.
Refrigerants with significantly lower GWP, such as CO2, have received increasing attention recently. Among these low GWP refrigerants, CO2 shows great potential and is seen as a possible final solution.
CO2 is safe and clean as it is non-toxic, non-flammable, has an ozone depletion potential (ODP) of 0, and a global warming potential of 1.
CO2 also has competitive cooling performance and excellent heating performance compared to other refrigerants. As a common byproduct of many industrial processes, CO2 is inexpensive and readily available. These unique properties make CO2 a promising refrigerant in refrigeration and heat pump systems.
The market scale is growing rapidly
Carbon dioxide heat pumps are mainly used in heating fields such as household water heaters, commercial heating, and automotive air conditioning. Among them, the development of carbon dioxide heat pump water heaters is particularly prominent in Japan.
As early as 2009, Japan took the lead in commercializing household carbon dioxide heat pump water heaters, demonstrating the huge potential of carbon dioxide heat pump water heaters and setting an example for global promotion and application.
Secondly, Europe is also a major market for tower heat pumps. The European government’s strict environmental regulations and supportive policies have driven the development of the market. As an important interpretation area of the tower heat pump market, the global tower heat pump water heater market is valued at US$1.69 billion in 2023 and is expected to increase from US$1.81 billion in 2024 to US$3.08 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate of 6.90% from 2024 to 2032.
The VMR report also shows that the CO2 heat pump water heater market size was US$1.65 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach US$2.8 billion by 2031, with a compound annual growth rate of 6.85% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2031.
The increasing demand for energy-saving water heaters in emerging economies has become the main factor driving the growth of the global carbon dioxide heat pump water heater market.
People’s requirements for quality of life are also getting higher and higher, and they pay more attention to the selection of energy-saving and environmentally friendly products.
CO2 heat pump technology has been applied in many fields in China.
The Beijing Workers’ Stadium introduced a CO2 heat pump hot water unit, which uses a transcritical cycle. For large stadiums, the demand for hot water varies greatly during events, and traditional hot water supply systems often have difficulty meeting these complex needs.
The CO2 heat pump hot water unit, with its flexible adjustment capability and efficient heating performance, accurately supplies hot water. It demonstrates the application potential of CO2 heat pumps in large public buildings and provides a reference example for other similar projects.
The clean heating project in Zhengding No. 1 Courtyard in Hebei Province provides clean and efficient heating services for a 130,000 square meter community using only two heat pump units. The success of the project proves the feasibility of carbon dioxide heat pumps in the field of civil heating.
In the field of transportation, CO2 heat pump technology has also made breakthrough progress. Volkswagen was the first to install a CO2 heat pump air conditioning system on its ID series models, which performs well in low temperature environments.
Carbon dioxide heat pump technology is becoming one of the important technologies in energy transformation. More and more companies are accelerating their layout in this field, showing a high degree of recognition of its huge potential and broad development prospects.
Pioneers of CO2 heat pump tech: Panasonic, Daikin and Mitsubishi
Since Panasonic developed the world’s first CO2 twin-rotor two-stage compressor in 2001, it has accumulated more than 1 million systems in the world.
Daikin’s products are widely used in home and commercial heating in the Japanese and European markets. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries’ Q-ton CO2 heat pump technology has shipped 3 million units in the Japanese market. Its products are known for their high efficiency and environmental protection characteristics and are gradually being promoted to the European market.
At present, Mercedes-Benz, Volkswagen, SAIC, Dongfeng Group, BAIC New Energy, NIO, FAW, etc. have carried out relevant research and launched carbon dioxide transcritical cycle automotive air conditioning systems. In the energy transformation, we look forward to seeing more companies stand out, promote carbon dioxide heat pump technology to a broader future, and contribute to global energy transformation and sustainable development.
 WhatsApp +8613906047998
WhatsApp +8613906047998