In recent years, heat pumps have become a notable alternative to traditional heating methods.
Unlike traditional systems that burn fossil fuels, heat pumps use renewable energy from the environment for heating, which can safely transfer heat between different locations, have low operating costs, and reduce environmental impacts.

Heat pump installed
What is a heat pump ?
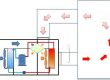
The heat pump uses a coolant with a boiling point as low as -30 to -40 ° C. Even in winter, it can absorb heat from outside and transfer this heat to provide heating indoors. In summer, some heat pumps work in reverse, effectively cooling the indoor temperature by expelling heat from outside the room.
Among various types of heat pumps, the most suitable one for household use is the heat pump that absorbs heat from outdoor air. They use fans to blow warm air indoors or heat water for radiators and floors.
These air source heat pumps also provide cooling in summer, making them an ideal choice for households in warmer climates. And other heat pumps use heat from underground pipelines or water bodies for heating.
Energy efficiency & costs
The issue of natural gas supply and the rise in natural gas prices have made household heating a focus of attention for improving efficiency and promoting energy independence.
Although heat pumps still use electricity, their efficiency is about 30% higher than traditional heating boilers. In Europe, natural gas is the main heating source, and higher natural gas prices mean that heat pump users can save more costs. Combining heat pumps with solar or wind energy can further reduce carbon emissions and create off grid systems.
Heat pumps not only have lower maintenance costs (only requiring professional inspections every 3-5 years), but are also safer, more reliable, and have a longer lifespan than traditional burner boilers
Current challenges
Although heat pumps have many advantages, they also have some drawbacks. The most noteworthy is the initial cost, which may be twice that of traditional heating boilers. Air source heat pumps are the most affordable and therefore most suitable for residential use.
In the past, heat pumps were difficult to function in cold weather conditions. However, the technological advancements made in recent years have enabled them to operate effectively even at temperatures as low as -25 ° C. There have always been concerns about the sustainability of the refrigerants used.
 WhatsApp +8613906047998
WhatsApp +8613906047998